
Tetrahydrocannabinol: Everything you need to know about Cannabis high element
If you have ever smoked a joint or consumed marijuana in any form, chances are you have experienced the effects of THC.
Known as tetrahydrocannabinol, it is the psychoactive compound found in cannabis plants responsible for the high sensation. The craziness you feel, the euphoria that takes over, the relaxation vibes, paranoia, and of course, the hunger – it is all because of THC.
THC is a cannabinoid (just like CBD) – one of the 113 found in the plant and comprises a significant proportion.
The recreational aspect of marijuana is driven by THC – it is also why marijuana is still illegal or regulated in many parts of the world – but luckily not in Thailand.
Let’s take a closer look into THC and understand this compound better.
How does THC interact with the body?
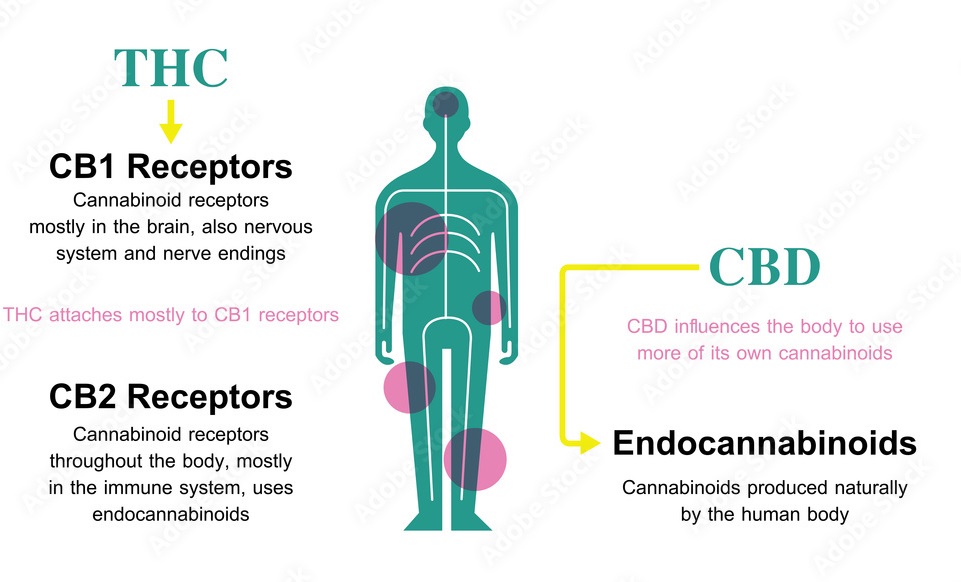
Like all cannabinoids, THC interacts with your body through the Endocannabinoid System (ECS).
If you are unfamiliar with ECS, don’t worry – we have covered this topic in great detail here. But just to give you a quick recap:
- It is a biological cell-signaling system present in your body, including the brain, organs, immune system, etc.
- It is involved in regulating many crucial processes like sleep, appetite, metabolism, mood, memory, pain, stress, inflammation, reproductive health, and more
- The ECS is responsible for maintaining the state of homeostasis (internal stability) in your body
The endocannabinoid system also has receptors (CB1 and CB2) placed all over your body. These receptors pick up the THC and other cannabinoids and affect the abovementioned areas.
Once inside your body, THC quickly binds to C1 & CB2 receptors across your body, effectively ‘taking control.’ This overwhelms the EC system, leading to the effects that we are all familiar with.
Effects of THC

THC will be felt from head to toe, given the widespread presence of ECS receptors in your body.
As a result, it can affect your body and mind in all sorts of manner, some more favorable than others. In some cases, negative effects can overwhelm the person, especially if they take too much THC, mix it with alcohol, or are inexperienced.
Effects vary from person to person and depend on the individual’s state of mind. If you have ever smoked marijuana with your friends, then you know what we are talking about. Some are hungry, some are just lying on the couch, others are laughing out loud, and then this one friend is freaking out.
Usual effects of THC:
- Feeling great, happy & laughter
- A relaxed and calm state of mind
- Reduced pain
- Enhanced senses and a general increase in awareness
- Perception of time slowing down, leading to slow reaction time
- Increased anxiety, paranoia and heartbeat
- Unable to remember things & bad at performing tasks
- Increased appetite/munchies
- Drowsiness
While these effects of THC are just short-term, consistent use of THC may alter how the ECS works over time. This may lead to problems with memory, addiction, and possibly mental health.
For this reason that marijuana users are often associated with poor memory.
But don’t let this one-sided image of THC scare you away. THC can be a great relaxant like all things in moderation – an amazing way to kick back after a long day at work. After all, it is euphoric and makes you feel happy!
Benefits of THC
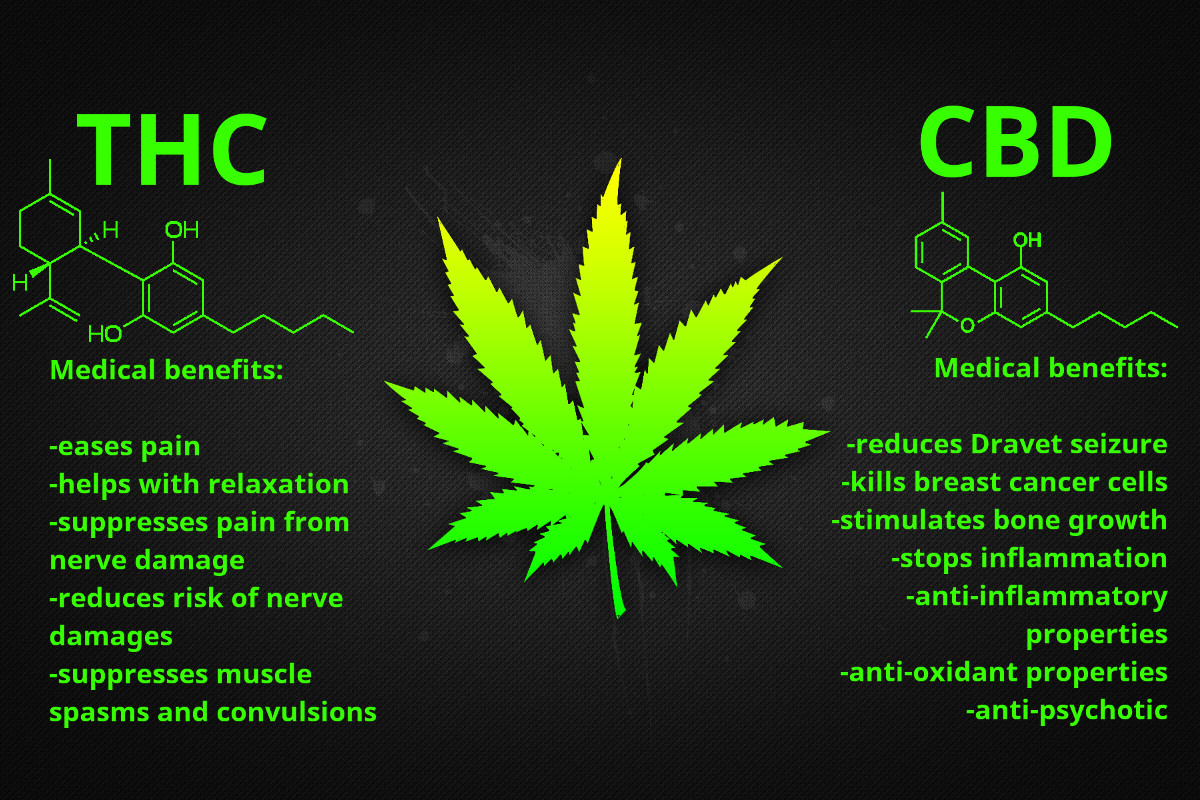
Like CBD, THC has also found its way into the world of medical marijuana. Scientific research and studies have shown promise for treating various ailments.
Some benefits of THC include:
- Effective sleep aid
- Provides pain relief
- Eases nausea and vomiting
- Increases appetite in patients suffering from HIV, hepatitis, cancer, etc.
- Relaxes muscles
In fact, the US Food and Drugs Administration (USFDA) has approved THC-based medications like dronabinol and nabilone to treat nausea and vomiting caused by chemotherapy.
Similarly, Sativex is another FDA-approved THC medicine used to treat pain from multiple sclerosis and neuropathic-related cancer.
The benefits of THC are still being studied, but from the data available so far, THC is not a compound to be discarded or ignored. Just like its CBD counterpart and its benefits, it can be great if used correctly.
How long does THC stay in your body?

Depending on how you consume marijuana – smoking, edibles, vaping – and your frequency of use, THC can stay in your system for anywhere between 1 to 30 days or more.
The reason being THC builds up in your system over time with regular use. So if you are a first-time user or someone who smokes pot every now and then, then THC can be detected up to three days after last use.
If you are a chronic user like Snoop Dogg who smokes THC every day, then it can be detected for up to 30 days and longer since last use.
And then there is also fact that edibles like weed cookies and brownies take a longer time to process in your body. Hence, they can stay longer in your body when compared to smoking a joint.
Is THC addictive?
Marijuana is addictive, and the main reason behind it is THC.
THC is addictive because it triggers the body to release more dopamine (the pleasure and satisfaction chemical). This increased level of dopamine due to marijuana triggers the brain to keep repeating this behaviour, which can lead to addiction.
Also referred to as ‘marijuana use disorder’, people can become dependent on cannabis and withdrawal symptoms may vary across irritability, mood swings, lack of proper sleep, low appetite, and other forms of physical discomfort etc.
These symptoms can last for up to two weeks after quitting before your body reaches back to normal.
Is THC legal in Thailand?
Smoking marijuana which makes you high is legal since the 9th of June 2022.
Medicinal marijuana is also legal in Thailand and products containing high levels of THC can be purchased, without the need for a prescription.
What is not legal is consuming concentrates with more than 0.2% of THC, such as cannabis oil, hash or dabbing.






Pingback: CBD Oil Dosage: How to Take Cannabis Oil and How Much You Need - Dr. CBD Innovation Center
Pingback: Ghost of New York City (NYC) Strain - Dr. CBD Innovation Center
Pingback: What are Terpenes - Dr. CBD Innovation Center
Pingback: Cinnamon Buddha Strain - Dr. CBD Innovation Center
Pingback: THC & CBD คืออะไร | ประโยชน์ทั้งสองสารมีอะไรบ้าง - Dr. CBD For Health
Pingback: CBD และ THC ในพืชกัญชา คืออะไร?? - Dr. CBD For Health
Pingback: ทำความรู้จัก กัญชงคืออะไร มีประโยชน์และสรรพคุณอย่างไร - Dr. CBD For Health
Pingback: What Are CBD Products? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding CBD - CBD For Health