Introduction
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a psychological disorder that can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It affects individuals differently and can have a significant impact on their daily lives. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an overview of PTSD, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and available treatments, as well as self-help strategies and resources for managing the condition.
Understanding PTSD
A. Definition and Overview: PTSD is a psychiatric disorder that occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It involves a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s mental and emotional well-being.
B. Common Causes and Traumatic Events: PTSD can result from various traumatic events, such as combat exposure, natural disasters, physical or sexual assault, accidents, or childhood abuse.
C. Prevalence and Risk Factors: PTSD can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. Certain factors, such as a history of trauma, lack of social support, or pre-existing mental health conditions, can increase the risk of developing PTSD.
D. How PTSD Differs from Normal Stress Response: While stress responses to traumatic events are normal, PTSD involves persistent and intrusive symptoms that significantly disrupt daily functioning and last for more than one month.
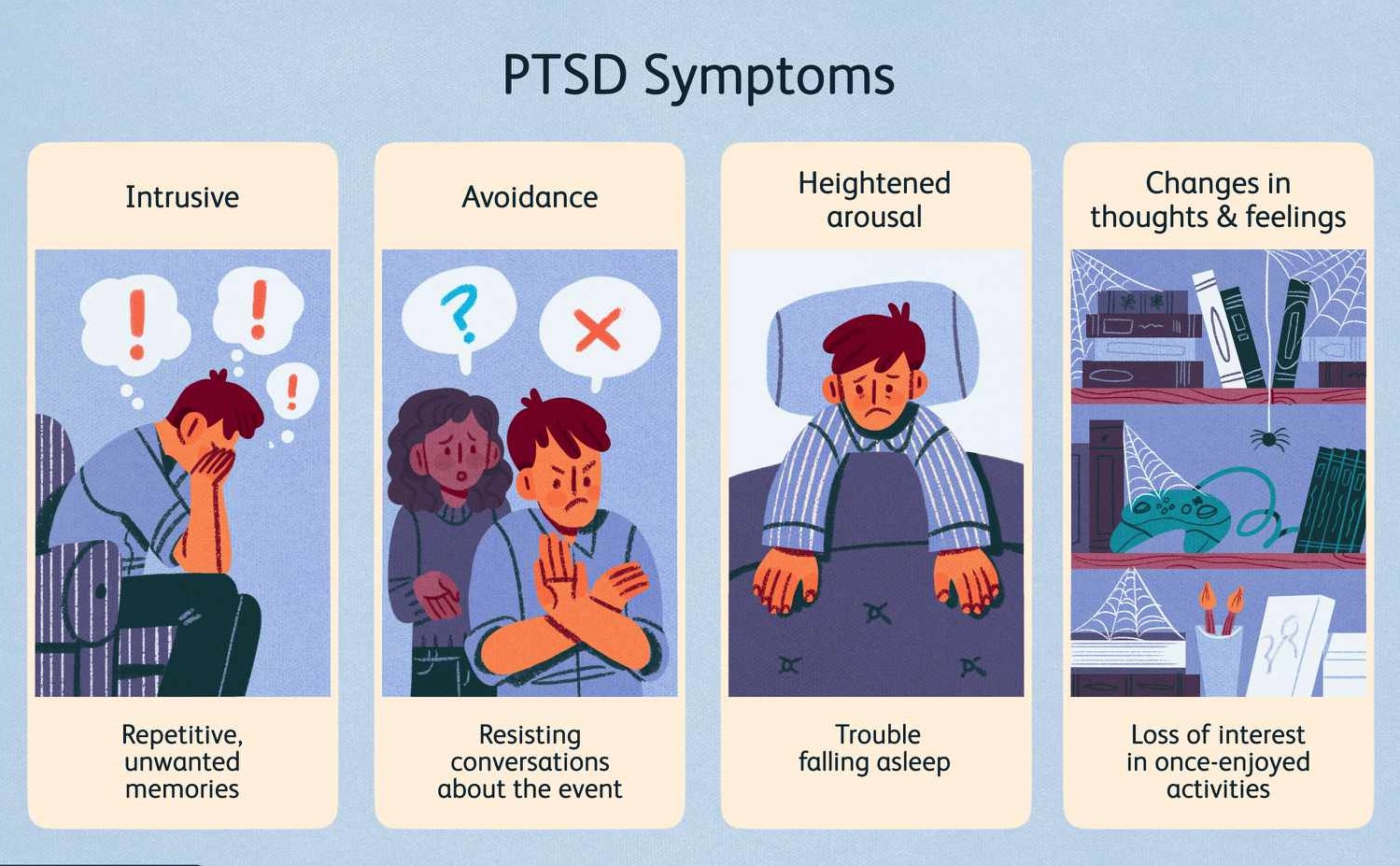
Symptoms of PTSD
A. Re-experiencing Symptoms: Flashbacks, nightmares, intrusive thoughts, and intense emotional or physical reactions triggered by reminders of the traumatic event.
B. Avoidance Symptoms: Avoiding places, activities, or people associated with the trauma, emotional numbness, and loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
C. Hyperarousal Symptoms: Hypervigilance, exaggerated startle response, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and sleep disturbances.
D. Cognitive and Mood Symptoms: Negative thoughts, distorted beliefs about oneself or the world, persistent feelings of guilt or shame, loss of memory related to the traumatic event, and changes in mood, such as depression or anxiety.
E. Duration and Severity of Symptoms: Symptoms may vary in intensity and duration, with some experiencing chronic symptoms while others have intermittent or delayed onset.
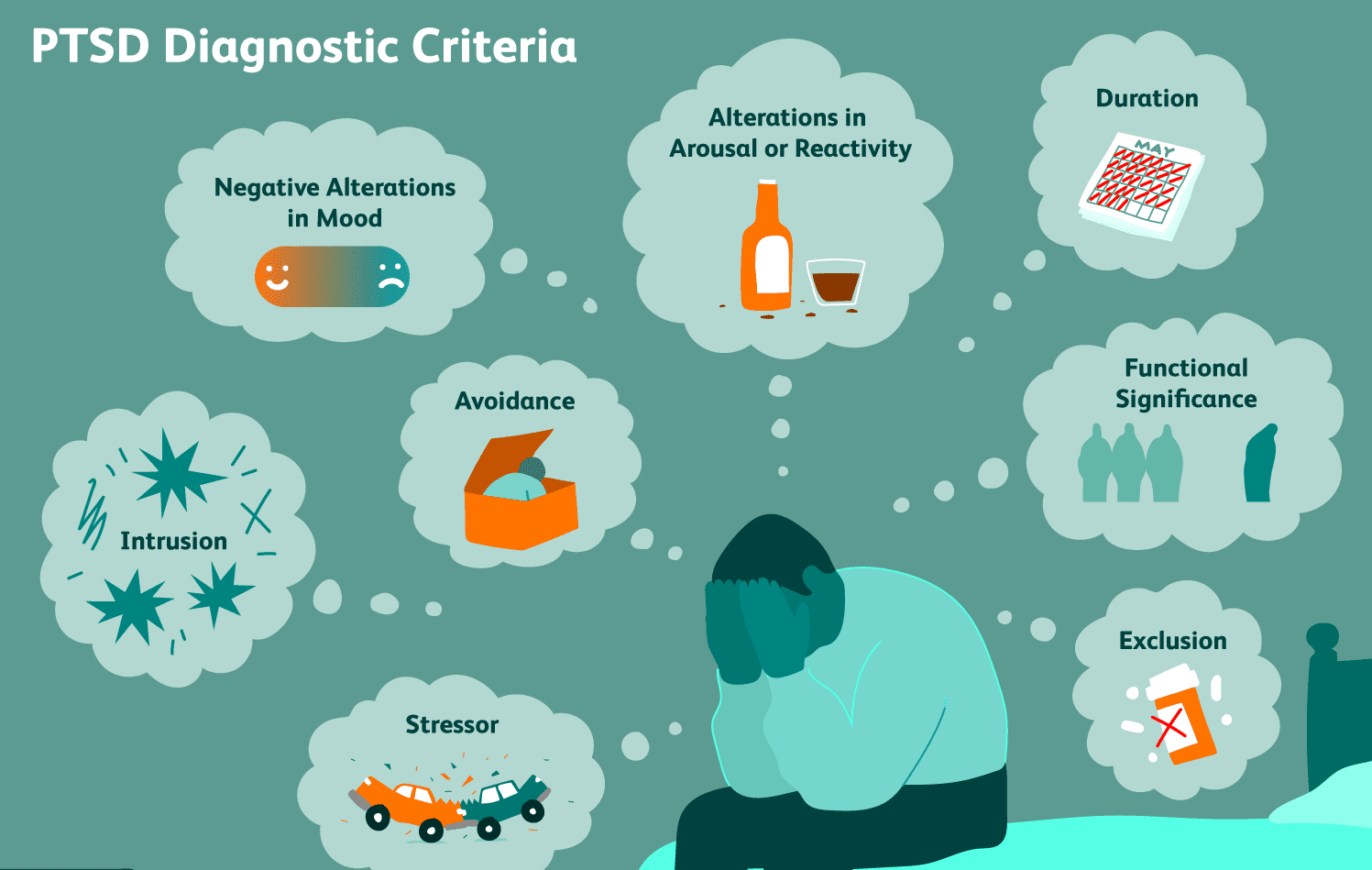
Diagnosis of PTSD
A. Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-5): The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) outlines specific criteria that clinicians use to diagnose PTSD, including the presence of re-experiencing, avoidance, arousal, and cognitive/mood symptoms, as well as the duration and impact on daily functioning.
B. Assessment and Screening Tools: Mental health professionals may use various assessment tools, questionnaires, and interviews to evaluate and diagnose PTSD.
C. Seeking Professional Help: If you suspect you have PTSD, it is important to consult a mental health professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for PTSD
A. Psychotherapy: Different psychotherapy approaches are effective in treating PTSD, including Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and modifying negative thoughts and behaviors; Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), which uses eye movements or other bilateral stimulation to process traumatic memories; Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE), which involves gradually confronting and processing traumatic memories; and group therapy or support groups that provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences and gain support.
B. Medications: Certain medications, such as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), and sometimes benzodiazepines, may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with PTSD.
C. Complementary and Alternative Therapies: Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies like yoga, acupuncture, mindfulness-based stress reduction, or art therapy. These approaches can help in managing symptoms and promoting overall well-being.
D. Innovative Treatments and Research: Ongoing research explores new treatment options for PTSD, such as virtual reality therapy, neurofeedback, and other innovative techniques.
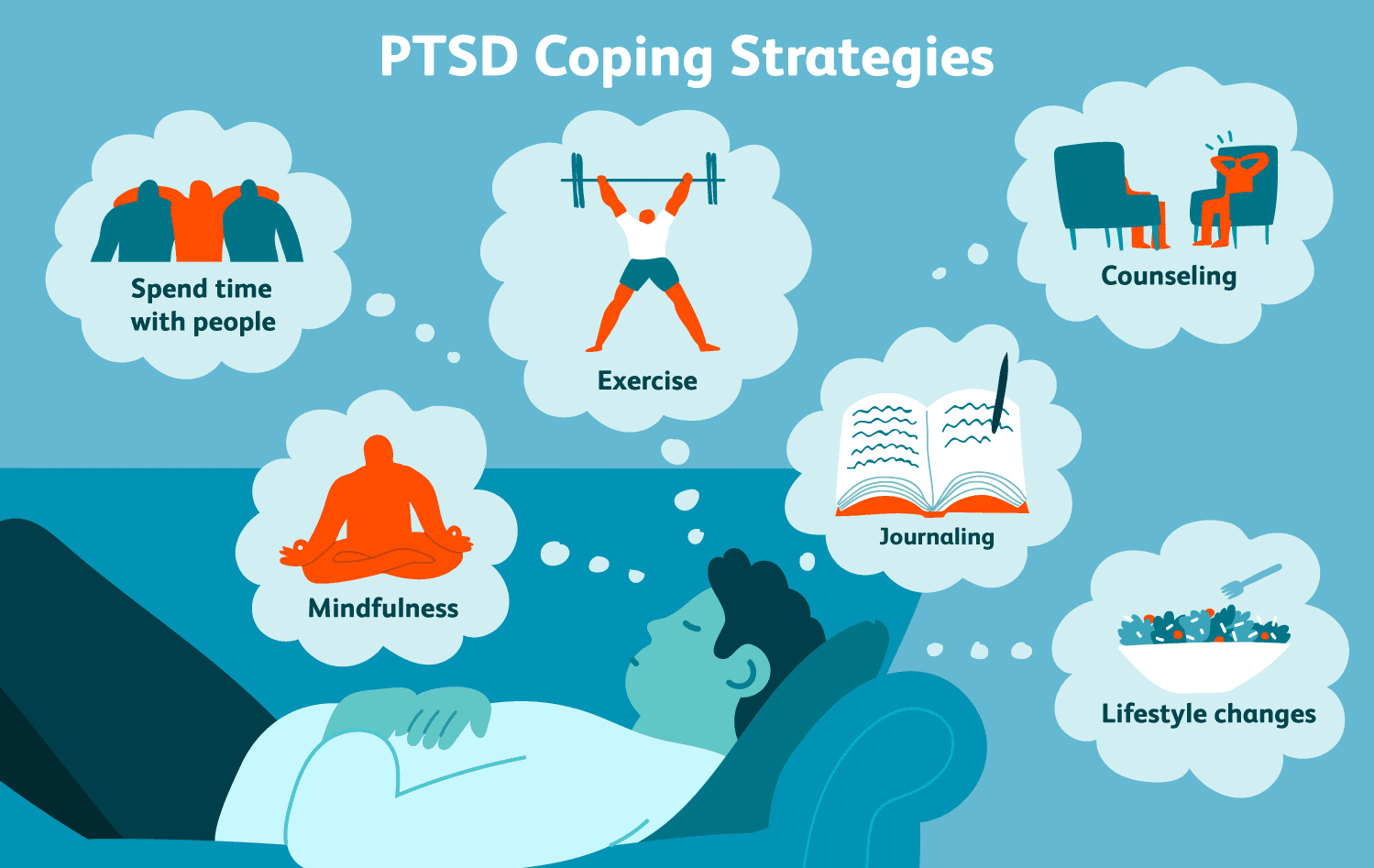
Self-Help Strategies for Managing PTSD
A. Establishing a Supportive Network: Surround yourself with understanding and supportive individuals who can offer empathy and assistance.
B. Practicing Stress Management Techniques: Learn and apply stress reduction techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation.
C. Engaging in Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote overall well-being.
D. Adopting Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Prioritize self-care by maintaining a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, avoiding excessive alcohol or substance use, and engaging in activities that bring you joy.
E. Exploring Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices can help increase present-moment awareness and reduce anxiety and intrusive thoughts associated with PTSD.
F. Creative Therapies and Expression: Engage in activities like art, writing, or music to express emotions and promote healing.
G. Seeking Social Support: Participate in support groups or online communities where you can connect with others who have experienced similar traumas.
Coping with Triggers and Flashbacks
A. Identifying Triggers: Recognize situations, people, places, or sensory stimuli that trigger distressing reactions or flashbacks.
B. Developing Coping Mechanisms: Work with a therapist to develop personalized coping strategies such as grounding techniques, relaxation exercises, and thought-stopping techniques.
C. Grounding Techniques: Engage your senses by focusing on the present moment, such as noticing specific objects, sensations, or sounds around you, to help anchor yourself during episodes of distress.
D. Relaxation and Breathing Exercises: Practice deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation during triggering situations.
Supporting a Loved One with PTSD
A. Educating Yourself about PTSD: Learn about PTSD symptoms, triggers, and available treatments to better understand and support your loved one.
B. Active Listening and Empathy: Provide a non-judgmental and empathetic listening ear, allowing your loved one to share their experiences and emotions.
C. Encouraging Professional Help: Encourage your loved one to seek professional help and offer to assist in finding suitable mental health resources.
D. Assisting with Daily Life and Routines: Help with practical tasks or provide emotional support when needed, as PTSD can affect daily functioning.
E. Promoting Healthy Coping Strategies: Encourage your loved one to engage in self-help strategies, attend therapy sessions, and practice self-care activities.
Resources and Support for PTSD
A. Mental Health Organizations: National and local mental health organizations can provide information, resources, and referrals for PTSD support and treatment.
B. Online Support Communities and Forums: Online communities allow individuals with PTSD to connect, share experiences, and offer support to one another.
C. Helplines and Crisis Intervention Services: Crisis hotlines and helplines provide immediate support and assistance for individuals experiencing distress or in crisis.
D. Books and Publications: Numerous books, articles, and publications offer in-depth information on PTSD, self-help strategies, and personal accounts of living with the condition.
E. Mobile Applications: Some smartphone applications are designed to assist individuals with PTSD in managing symptoms, tracking mood, and practicing relaxation techniques.
Conclusion
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is a complex condition that requires understanding, support, and appropriate treatment. By recognizing the symptoms, seeking professional help, and utilizing self-help strategies, individuals with PTSD can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and work towards recovery. Remember, recovery takes time, and each person’s journey is unique.





