Introduction
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While mild anxiety can be a normal response to stressful situations, excessive and persistent anxiety can significantly impact an individual’s well-being. Anxiolytic effects refer to the ability of certain substances, therapies, and lifestyle changes to reduce anxiety symptoms and promote a sense of calm and relaxation. This comprehensive guide aims to explore various anxiolytic approaches to help individuals better understand and manage anxiety.
Table of Contents
Understanding Anxiety
A. Types of Anxiety Disorders: This section delves into different types of anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder (SAD), and specific phobias.
B. Causes and Triggers: Explore the various factors that can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, including genetic predisposition, environmental stressors, trauma, and imbalances in brain chemistry.
C. Symptoms of Anxiety: Detail the common physical, cognitive, and emotional symptoms associated with anxiety disorders, such as excessive worrying, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, increased heart rate, and muscle tension.
Anxiolytic Effects Explained
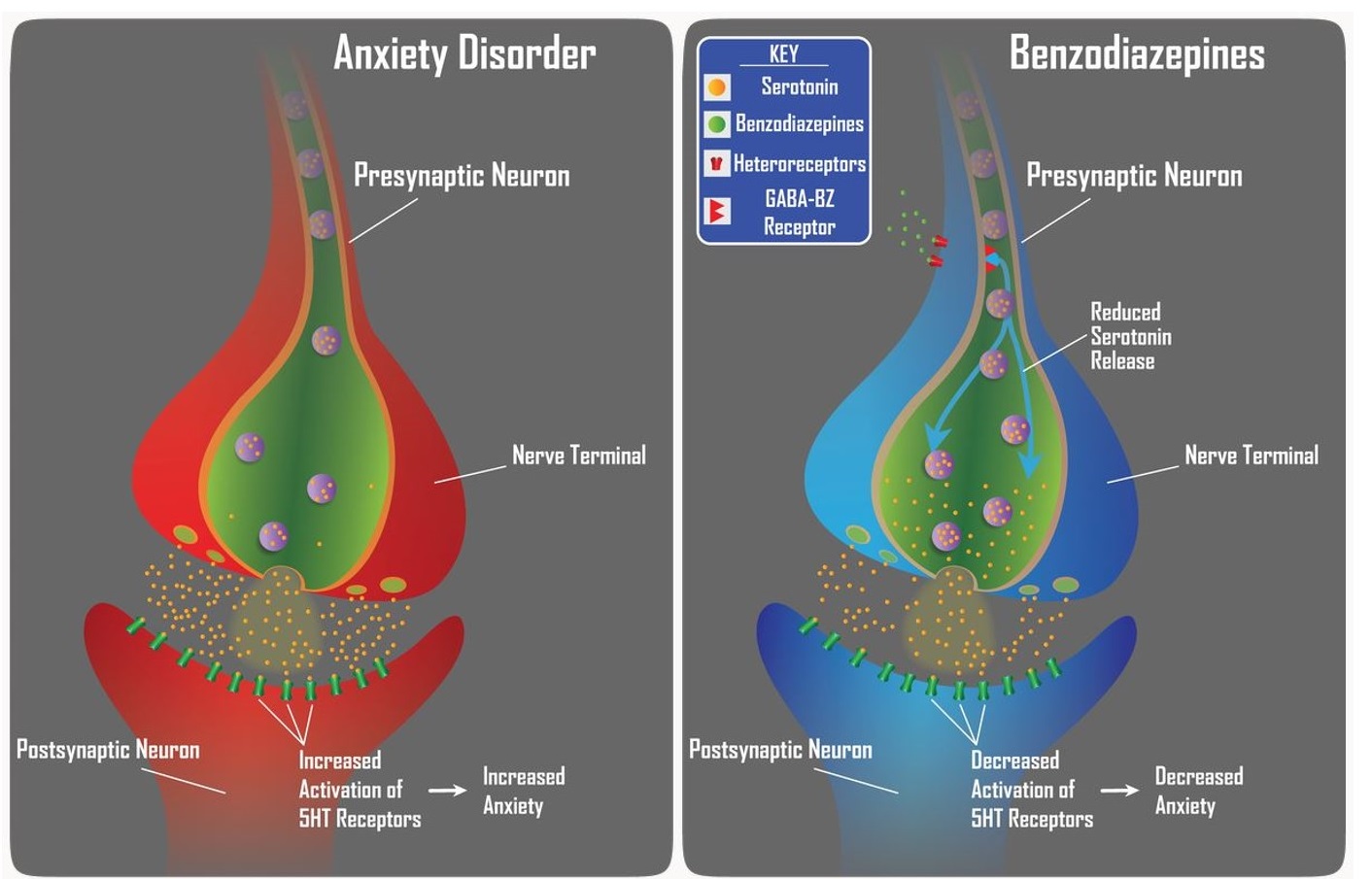
A. How Anxiolytics Work: Provide an overview of the mechanisms by which anxiolytic substances and therapies exert their effects on the brain and body, including modulation of neurotransmitters and the limbic system.
B. Different Classes of Anxiolytic Substances: Discuss the main categories of anxiolytic substances, such as benzodiazepines, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and herbal remedies like kava and valerian.
Natural Anxiolytic Approaches
A. Lifestyle Modifications: Highlight the importance of healthy lifestyle habits in managing anxiety, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
B. Relaxation Techniques: Explore various relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and mindfulness meditation, which can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
C. Herbal Remedies and Supplements: Provide an overview of herbal remedies and supplements with potential anxiolytic effects, such as chamomile, lavender, passionflower, and omega-3 fatty acids, while emphasizing the importance of consulting a healthcare professional before use.
Pharmaceutical Anxiolytic Medications
A. Benzodiazepines: Explain the mechanism of action, potential side effects, and considerations associated with benzodiazepines, which are commonly prescribed for short-term relief of severe anxiety symptoms.
B. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): Detail the role of SSRIs in the treatment of anxiety disorders, including their effectiveness, potential side effects, and considerations for long-term use.
C. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Discuss SNRIs as an alternative class of antidepressant medications that may be prescribed for certain anxiety disorders.
D. Other Medications: Briefly touch upon other medications, such as beta-blockers and anticonvulsants, which may be prescribed in specific cases of anxiety disorder.
Psychotherapy and Counseling
A. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Explain how CBT helps individuals identify and modify negative thought patterns and behaviors contributing to anxiety, and highlight its evidence-based effectiveness.
B. Exposure Therapy: Describe exposure therapy as a technique that gradually exposes individuals to anxiety-provoking situations to help reduce their fear and anxiety responses.
C. Mindfulness-Based Therapies: Introduce mindfulness-based approaches like mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), which promote non-judgmental awareness and acceptance of present-moment experiences.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
A. Acupuncture: Explore the use of acupuncture, an ancient Chinese practice involving the insertion of thin needles at specific points on the body, which may help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
B. Yoga and Meditation: Detail the benefits of yoga and meditation in reducing anxiety through physical postures, controlled breathing, and relaxation techniques.
C. Massage Therapy: Explain how massage therapy can promote relaxation, relieve muscle tension, and reduce anxiety symptoms.
D. Aromatherapy: Discuss the potential anxiolytic effects of essential oils, such as lavender and bergamot, when used in aromatherapy practices.
Lifestyle Practices for Managing Anxiety
A. Regular Exercise: Highlight the positive impact of physical exercise on anxiety reduction, including the release of endorphins and the regulation of stress hormones.
B. Healthy Diet: Discuss the importance of a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids in supporting overall mental health and managing anxiety.
C. Sufficient Sleep: Emphasize the role of adequate sleep in regulating mood, reducing anxiety, and providing overall well-being.
D. Stress Management Techniques: Provide practical strategies for managing stress, such as time management, setting boundaries, and engaging in hobbies and activities that promote relaxation.
E. Social Support and Connection: Highlight the significance of nurturing supportive relationships and seeking social connections as a means of reducing anxiety and fostering a sense of belonging.
Self-Help Strategies for Anxiety
A. Deep Breathing Exercises: Explain various deep breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing and box breathing, which can activate the body’s relaxation response.
B. Progressive Muscle Relaxation: Detail the step-by-step process of progressively tensing and relaxing muscle groups to promote physical and mental relaxation.
C. Journaling: Encourage the practice of keeping a journal to express emotions, identify triggers, and gain insights into patterns of anxiety.
D. Time Management and Prioritization: Provide practical tips on managing time effectively and prioritizing tasks to reduce feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.
E. Seeking Professional Help: Encourage individuals to reach out to mental health professionals for personalized guidance and support.
Seeking Professional Help
A. Choosing a Mental Health Professional: Guide readers in selecting the right mental health professional, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, or counselors, based on their specific needs.
B. Treatment Planning and Monitoring: Explain the importance of developing a comprehensive treatment plan with a mental health professional and regularly monitoring progress.
C. Collaboration with Healthcare Providers: Highlight the significance of open communication and collaboration between individuals and healthcare providers to optimize anxiety management and ensure holistic care.
Conclusion
Summarize the key takeaways from the guide, emphasizing the importance of an individualized approach to managing anxiety and the significance of seeking professional guidance when needed.
Note: It’s important to remember that this guide serves as an informational resource and should not replace professional advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.





